What is Good Oral Hygiene?
Good oral hygiene results in a mouth that looks and smells healthy. This means:
- Your teeth are clean and free of debris.
- Gums are pink and do not hurt or bleed when you brush or floss.
- Bad breath is not a constant problem.
If our gums do hurt or bleed while brushing or flossing, or we are experiencing persistent bad breath, see our dentist. Any of these conditions may indicate a problem.
Our dentist or hygienist can help us learn good oral hygiene techniques and can help point out areas of our mouth that may require extra attention during brushing and flossing.
How is Good Oral Hygiene Practiced?
Maintaining good oral hygiene is one of the most important things you can do for your teeth and gums. Healthy teeth not only enable you to look and feel good, but they also make it possible to eat and speak properly. Good oral health is important to your overall well-being.

Daily preventive care ![]() , including proper brushing and flossing, will help stop problems before they develop and is much less painful, expensive, and worrisome than treating conditions that have been allowed to progress.
, including proper brushing and flossing, will help stop problems before they develop and is much less painful, expensive, and worrisome than treating conditions that have been allowed to progress.


- Oral hygiene is defined as the condition or practice of maintaining the tissue and structures of mouth in a healthy state.
- As oral health affects the overall health of an individual it is therefore of paramount importance to maintain oral hygiene.

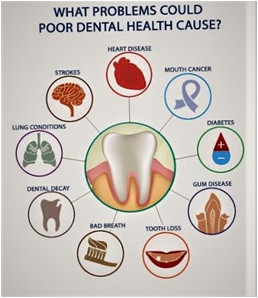
A clean mouth and properly functioning teeth are essential for physical and mental well being. Research indicates that a clean mouth prevents pneumonia, gum disease, and help prevent heart disease.
Oral care prevents infection in the mouth by removing food particles and plaque and stimulate the circulation to gums .it prevents halitosis
SOME COMMON ORAL PROBLEMS
DENTAL CARIES/DECAY
Tooth decay is a process that results in the gradual destruction of a tooth and is caused by a combination of bacteria (dental plaque) and sugar diet
Warning signs-
- Tooth covered in food and debris
- Holes in tooth
- Broken teeth
- Discolored teeth
- Tooth sensitivity in hot and cold food
- Difficulty in mastication
- Toothache bad breath swelling in face and jaw area
HOW TO PREVENT
- Brushing twice with fluoride toothpaste
- Regular cleaning between the tooth
- Reduction in sweetened foods and drinks especially in between meals
- Regular professional checkups and cleaning
- Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and avoid vigorous brushing
- Use fluoride toothpaste
- Glass monomer cement restoration

ROOT CARIES AND DECAY
Gums recede due to damage caused by hard brushing and gum disease. It causes exposure of root surface
WARNINGS:
- Receded gums
- Pits and dark colouration near the cervical area
- Halitosis
- Difficulty in eating

ATTRITION AND ABRASION
- This is due to exposed dentine being exposed
- Usually occurs in form of pieces of the tooth breaking away from breakings, tooth chippings and sharp to the tongue
HOW TO PREVENT:
- Regular dental checkups are important.

GUM DISEASE
- GINGIVITIS
- A mild form of gum disease not painful, if untreated can convert in periodontitis due to lack of proper brushing and cleaning between the tooth.
WARNING SIGNS:
- Red swollen gums or tender gums
- Bad breath
- Bleeding while brushing and flossing
HOW TO PREVENT:
- Brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste
- Regular cleaning between the tooth
- Regular dental checkups

It is a destructive form of gum disease. There is an inflammatory response that destroys periodontal fibers and bone supporting teeth.
WARNING SIGN
- Red swollen or tender gums
- Receding gingiva
- Loose teeth
- Pus between gum and teeth
- Bad breath
- Change in the fit of partial denture
HOW TO PREVENT:
- Brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste
- Regular professional checkups

Dry mouth or xerostomia is a condition where the mouth becomes dry due to reduced salivary flow. It is caused due to a certain medical condition as Sjogren’s or Alzheimer’s or due to antihistaminics diuretics or antidepressants.
WARNING SIGNS
- Difficulty in swallowing or speaking
- Dryness in mouth
- Burning sensation or sore feeling in the mouth
- Bad breath
HOW TO PREVENT
- Follow strict daily oral hygiene with fluoride toothpaste
- Salt and bicarbonate rinses
- Proper medication
HOW TO PREVENT:
- Use of topical analgesic
- Replacement of broken restoration
- Adjustment of poorly fit dentures
- ULCER LASTING MORE THAN TWO WEEKS NEED TO BE CHECKED BY DENTIST

- TOOTHBRUSHES
- FOAM SWABS WITH CHLORHEXIDINE
- MOUTH SQUARE
- FLOURIDE TOOTHPASTE
- SODIUM BICARBONATE RINSES
- CHLORHEXIDINE MOUTHWASHES
- FLOSSING
- DENTURE CARE

TIPS FOR ORAL HEALTH:
- WIPE THE BABY GUMS AFTER EVERY FEED (BEFORE ERUPTION OF TEETH)
- MASSAGE GUMS AND TEETH WITH MILD PRESSURE (DURING TEETHING)
- BRUSH WITH SILICONE FINGER TOOTHBRUSH (AFTER TEETH ERUPTION)

